What is Coaxial Cable? Where is it used?
What is Coaxial Cable? Where is it used? is an energy current carrying product that is covered with an insulating material and has one or more metallic conductors in it, which is used in the fields of electricity and electronics. Coaxial cable can also be defined as a type of copper cable used in environmental conditions where electrical noise is intense. The use of copper is preferred in most networks, since copper’s low resistance to electric current allows signals to be carried farther.
Coaxial cables have a high capacitance value. Television, telephone networks, local area networks and CATV (Community Antenna Television) are among the application areas of coaxial cables. Although these cables are used in long distance telephone networks, they have been replaced by fiber optic cables and satellite systems in this field. Today, coaxial cables are used in television and camera systems and are used in the transmission of high frequency signals of radio, television and telephones. Coaxial cables are also very efficient at carrying high frequency analog signals.
Because of their features, coaxial cables are used for data transmission in residential, commercial and industrial facilities. Coaxial cables, which have been used since 1940, have 80 times faster information transmission capacity and higher bandwidth than twisted wires. At the same time, it provides more protection against electrical noise and shocks. Coaxial cables, which can carry both analog and digital signals, can also provide an advantageous use in cable TV broadcasts due to their high bandwidth.
Structural Properties of Coaxial Cables
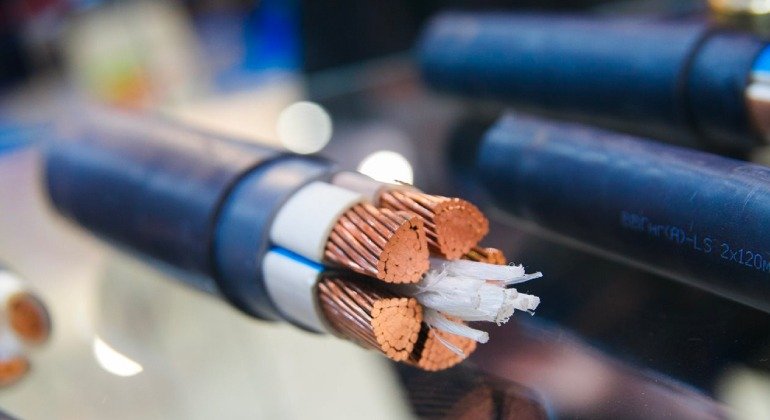
Coaxial cables have conductive copper at their core. Copper is covered with an insulating layer from the outside, and the top of the layer is covered with aluminum or copper braided armor. On the armor, there is an insulating outer plastic coating. Thanks to the structure of the coaxial cable, the signal carried on the central conductor is not affected by electrical noises.
The dense metal shielding inside the coaxial cable acts as a barrier against electromagnetic radiation and forms a flexible cylinder around the inner cable. This barrier provides insulation of the inner cable in two different ways:
● Shields the cable from electromagnetic field that can cause interference. It prevents other cables from being affected by the electromagnetic field produced by the inner cable.
● Since the cable in the center is constantly protected in the same way and distance on the outer protective side, it is prevented from being affected by the bends or twists at the corners in parallel laying.
Coaxial cables are known as a type of cable developed to transmit low-power signals in areas with high electromagnetic pollution. There are different types of coaxial cables with different properties. In computer networks, it is possible to provide communication over longer distances than UTP or STP cables without requiring repeaters. In coaxial cables, data is carried by the wire in the center. The inner conductor wire and the outer conductor wire generally carry currents of the same magnitude in opposite directions. According to the application areas of coaxial cables, inner conductor, outer conductor and outer insulator materials are collected in three basic groups: coaxial cables according to the inner conductor, coaxial cables according to the outer conductor and coaxial cables according to the plastic outer sheath.
Coaxial Cables by Inner Conductor
In coaxial cables, data transmission is provided through an inner conductor. Coaxial cables, in which pure copper conductors are inner conductors, are used in closed circuit television system installations and have less line loss and deterioration risk in the signal compared to copper-clad steel conductors. Since pure copper is soft, it should be used by being fixed in the installations so that there is no break in the inner conductor in case of moving breaks.
Stranded conductors are obtained by winding many fine pure copper wires together. Coaxial cables with copper-clad steel conductors are used in areas requiring strength. Since the inner conductor is steel, they are known to be resistant to breakage.
Coaxial Cables by Outer Conductor
They are used to prevent electromagnetic interference and radio frequency effects in the external environment. In the braided coating conductor, the conductive strips consisting of copper-tin alloy, aluminum and pure copper depending on the coating are brought together in such a way that they are intertwined and an outer conductor is obtained.
Coaxial cables, in which the aluminum foil braided coating conductor is the outer conductor, are generally used in CATV installations, and the outer conductor is 100% aluminum foil. The four-layer cladding conductor is obtained by sequentially combining the braided cladding conductor and the aluminum foil conductor and forming four layers. It is preferred to be used in environments where electronic interference effect is high.
Coaxial Cables by Plastic Coating
The outer plastic coating serves as thermal electrical insulation between the environment and the cable in coaxial cables. Plastic outer coating types are formed according to the ambient temperature and electrical resistance properties.
It is one of the outer insulators of PVC coaxial cables and can be used in areas between -40 and +80 degrees. In areas where external insulators made of polyethylene with very high electrical insulators will be used, the ambient temperature should be between -55 and +85 degrees. External insulators made of fluorinated ethylene propylene, which are very resistant to chemicals and heat, can be used in places with temperatures between -50 and +200 degrees.
Types of coaxial cables have their own RG codes. It is known that what matters and changes in coaxial cables is the impedance or ohmmeter of the cable. Impedance is the resistance of the cable against a certain length of electric current.